There are different ways of scraping web pages using python. In my previous article, I gave an introduction to web scraping by using the libraries:requests and BeautifulSoup. However, many web pages are dynamic and use JavaScript to load their content. These websites often require a different approach to gather the data.
In this tutorial, I will present several different ways of gathering the content of a webpage that contains Javascript. The techniques used will be the following:
-
Using selenium with Firefox web driver
-
Using a headless browser with phantomJS
-
Making an API call using a REST client or python requests library
TL;DR For examples of scraping javascript web pages in python you can find the complete code as covered in this tutorial over on GitHub.
Update November 7th 2019: Please note, the html structure of the webpage being scraped may be updated over time and this article initially reflected the structure at the time of publication in November 2018. The article has now been updated to run with the current webpage but in the future this may again change.
First steps
To start the tutorial, I first needed to find a website to scrape. Before proceeding with your web scraper, it is important to always check the Terms & Conditions and the Privacy Policy on the website you plan to scrape to ensure that you are not breaking any of their terms of use.
Motivation
When trying to find a suitable website to demonstrate, many of the examples I first looked at explicitly stated that web crawlers were prohibited. It wasn’t until reading an article about sugar content in yogurt and wondering where I could find the latest nutritional information inspired another train of thought where I could find a suitable website; online supermarkets.
Online retailers often have dynamic web pages that load content using javascript so the aim of this tutorial is to scrape the nutritional information of yogurts from the web page of an online supermarket.
Setting up your environment
Since we will be using some new python libraries to access the content of the web pages and also to handle the data, these libraries will need to be installed using your usual python package manager pip. If you don’t already have beautifulsoup then you will need to install this here too.
pip install selenium
pip install pandas
To use selenium as a web driver, there are a few additional requirements:
Firefox
I will be using Firefox as the browser for my web driver so this means you will either need to install Firefox to follow this tutorial or alternatively you can use Chromium with Chrome.
Geckodriver
To use the web driver we need to install a web browser engine, geckodriver. You will need to download geckodriver for your OS, extract the file and set the executable path location.
You can do this in several ways:
-
Move geckodriver to a directory of your choice and define this the executable path in your python code (see later example),
- Move geckodriver to a directory which is already a set as a directory where executable files are located, this is known as your environmental variable path.
You can find out which directories are in your $PATH by the following:
- Windows
Go to:
Control Panel > Environmental Variables > System Variables > Path - Mac OSX / Linux
In your terminal use the command:
echo $PATH
- Windows
-
Add geckodriver location to your PATH environment variables
-
Windows
Go to:
Control Panel > Environmental Variables > System Variables > Path > Edit
Add the directory containing geckodriver to this list and save -
Mac OSX / Linux
Add a line to your .bash_profile (Mac OSX) or .bash_rc (Linux)# add geckodriver to your PATH export PATH="$PATH:/path/to/your/directory"Restart your terminal and use the command from 2. to check that your new path has been added.
-
PhantomJS
Similar to the steps for geckodriver, we also need to download PhantomJS. Once downloaded, unzip the file and move to a directory of choice or add to your path executable, following the same instructions as above.
REST Client
In the final part of this blog, we will make a request to an API using a REST client. I will be using Insomnia but feel free to use whichever client you prefer!
Scraping the web page using BeautifulSoup
Following the standard steps outlined in my introductory tutorial into web scraping, I have inspected the webpage and want to extract the repeated HTML element:
<div data-cid="XXXX" class="listing category_templates clearfix productListing ">...</div>
As a first step, you might try using BeautifulSoup to extract this information using the following script.
# import libraries
import urllib.request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# specify the url
urlpage = 'https://groceries.asda.com/search/yogurt'
print(urlpage)
# query the website and return the html to the variable 'page'
page = urllib.request.urlopen(urlpage)
# parse the html using beautiful soup and store in variable 'soup'
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, 'html.parser')
# find product items
# at time of publication, Nov 2018:
# results = soup.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'listing category_templates clearfix productListing'})
# updated Nov 2019:
results = soup.find_all('div', attrs={'class': 'co-product'})
print('Number of results', len(results))
Unexpectedly, when running the python script, the number of results returned is 0 even though I see many results on the web page!
https://groceries.asda.com/search/yoghurt
BeautifulSoup - Number of results 0
When further inspecting the page, there are many dynamic features on the web page which suggests that javascript is used to present these results. By right-clicking and selecting View Page Source there are many
The first approach to scrape this webpage is to use Selenium web driver to call the browser, search for the elements of interest and return the results.
Scraping the web page using Selenium
-
Selenium with geckodriver
Since we are unable to access the content of the web page using Beautiful Soup, we first need to set up a web driver in our python script.
# import libraries import urllib.request from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from selenium import webdriver import time import pandas as pd # specify the url urlpage = 'https://groceries.asda.com/search/yogurt' print(urlpage) # run firefox webdriver from executable path of your choice driver = webdriver.Firefox(executable_path = 'your/directory/of/choice')As mentioned when installing geckodriver, if the executable file is not in an executable path, we are able to define the path in our python script. If it is in an executable path then the line above becomes:
# run firefox webdriver from executable path of your choice driver = webdriver.Firefox()Once set up, we can now connect to the web page and find the elements of interest. When loading the webpage in a browser, results often take a while to load and also may not even load until we scroll down the page. With this in mind, here we can add some javascript for the web driver to execute to perform such actions. Below is a simple example to get the page to scroll, there will be more efficient ways to do this, why not test your own javascript here and let me know in the comments what works best for you!
We also add a sleep time as another method to wait for the page to fully load.
# get web page driver.get(urlpage) # execute script to scroll down the page driver.execute_script("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight);var lenOfPage=document.body.scrollHeight;return lenOfPage;") # sleep for 30s time.sleep(30) # driver.quit()If we run the script now (you can also uncommentdriver.quit() at the end to ensure the browser closes), as your python script runs Firefox will open the url specified and scroll down the page. Hopefully, you should many products load up before the script finishes running.
Next, we want to get the elements of interest. Previously, using Beautiful Soup we have tried to find all elements based on the tag and class attributes, however, in this example we will use a slightly different approach to access the product information. Instead, we can search for the elements by xpath, based on the XML structure or the css selector.
We can inspect the element of interest and within the toolbar, right-click on the highlighted element and Copy > Copy xpath (or Copy Selector). This is another interesting way to understand the structure of the html. In this case we will be using the xpath to find the elements, and we can then print the number of results that match:
# find elements by xpath # at time of publication, Nov 2018: # results = driver.find_elements_by_xpath("//*[@id='componentsContainer']//*[contains(@id,'listingsContainer')]//*[@class='product active']//*[@class='title productTitle']") # updated Nov 2019: results = driver.find_elements_by_xpath("//*[@class=' co-product-list__main-cntr']//*[@class=' co-item ']//*[@class='co-product']//*[@class='co-item__title-container']//*[@class='co-product__title']") print('Number of results', len(results))One of the main reasons for using the xpath rather than using the element as the results have a few elements where the stem of the id is listingsContainer with some additional words, so the contains function has been used to select all of the results but also to exclude any of the other div elements within the container such as for adverts.
Firefox Webdriver - Number of results 38Now that we have some results from the page, we can loop over each result and save the data of interest. In this case, we can save the product name and link.
Note that there are actually more than 38 results on the web page. This number also may vary depending on how many results load when you connect to the page. All results can be gathered by either changing the javascript we execute as suggested above, alternatively other methods will be explored in the following sections.
# create empty array to store data data = [] # loop over results for result in results: product_name = result.text link = result.find_element_by_tag_name('a') product_link = link.get_attribute("href") # append dict to array data.append({"product" : product_name, "link" : product_link})Outside of this loop, we can close the browser and as we imported the pandas library, we can make use of that by saving the data we have scraped to a dataframe. We can print the dataframe to view the content.
# close driver driver.quit() # save to pandas dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data) print(df)In this format, we can very simply write this data to a csv.
# write to csv df.to_csv('asdaYogurtLink.csv')Using Selenium with geckodriver is a quick way to scrape the web pages that are using javascript but there are a few drawbacks. I have found that sometimes the page does not load (I’m sure that this could be more efficient by changing the javascript we execute as mentioned above, but I am new to JS so this might require some time), but also loading the browser and waiting for the page to load takes time.
Another option, we can use a headless browser. This should speed up the scraping as we don’t have to wait for the browser to load each time.
-
Selenium with a headless browser
When using PhantomJS as a headless browser instead of geckodriver, the only difference is how the web driver is loaded. This means that we can follow the method above but change the line that initialises the web driver which becomes:
# run phantomJS webdriver from executable path of your choice driver = webdriver.PhantomJS(executable_path = 'your/directory/of/choice')Note here that Selenium support for PhantomJS has been depreciated and provides a warning.
It is also possible to use headless mode with geckodriver by using the headless option:
from selenium import webdriver from selenium.webdriver.firefox.options import Options options = Options() options.headless = True driver = webdriver.Firefox(firefox_options=options, executable_path = 'your/directory/of/choice')By using the headless browser, we should see an improvement in time for the script to run since we aren’t opening a browser but not all results are scraped in a similar way to using firefox webdriver in normal mode.
Making an API request
The final approach we will discuss in this tutorial is making a request to an API. When inspecting the Network page XHR files, as a page loads this page displays the requests that are being made. Within this list is a /search request which calls an API endpoint to get the results that are presented on the page.
We are able to make the same request using either a REST client or with a few lines of python.
If we inspect the search file and look at the headers, the request url containing the keyword and other parameters that are needed to make the request. Below the general details are the response and request headers which we may need later.
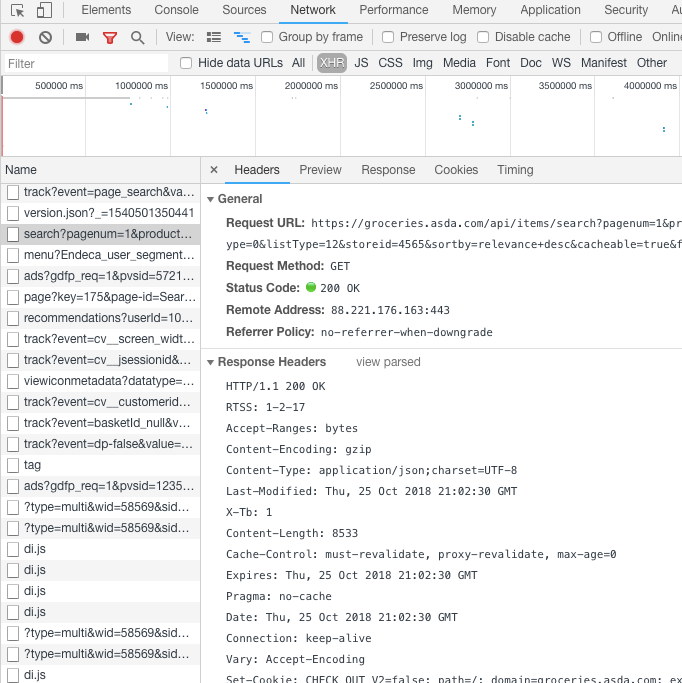 Inspect tool showing the search request headers
Inspect tool showing the search request headers
To get the response, we can take the request url and as a test enter this into the address bar of your browser. Since the parameters are added in the string we can also try to remove all but the keyword parameter to test whether any further parameters are required. In this case, the keyword query returns the results in the browser, so we can also perform the same request using a REST client or in python.
Insomnia REST client
Using insomnia we can enter the request url and send the request.
This returns a JSON response containing the data that we are looking for!
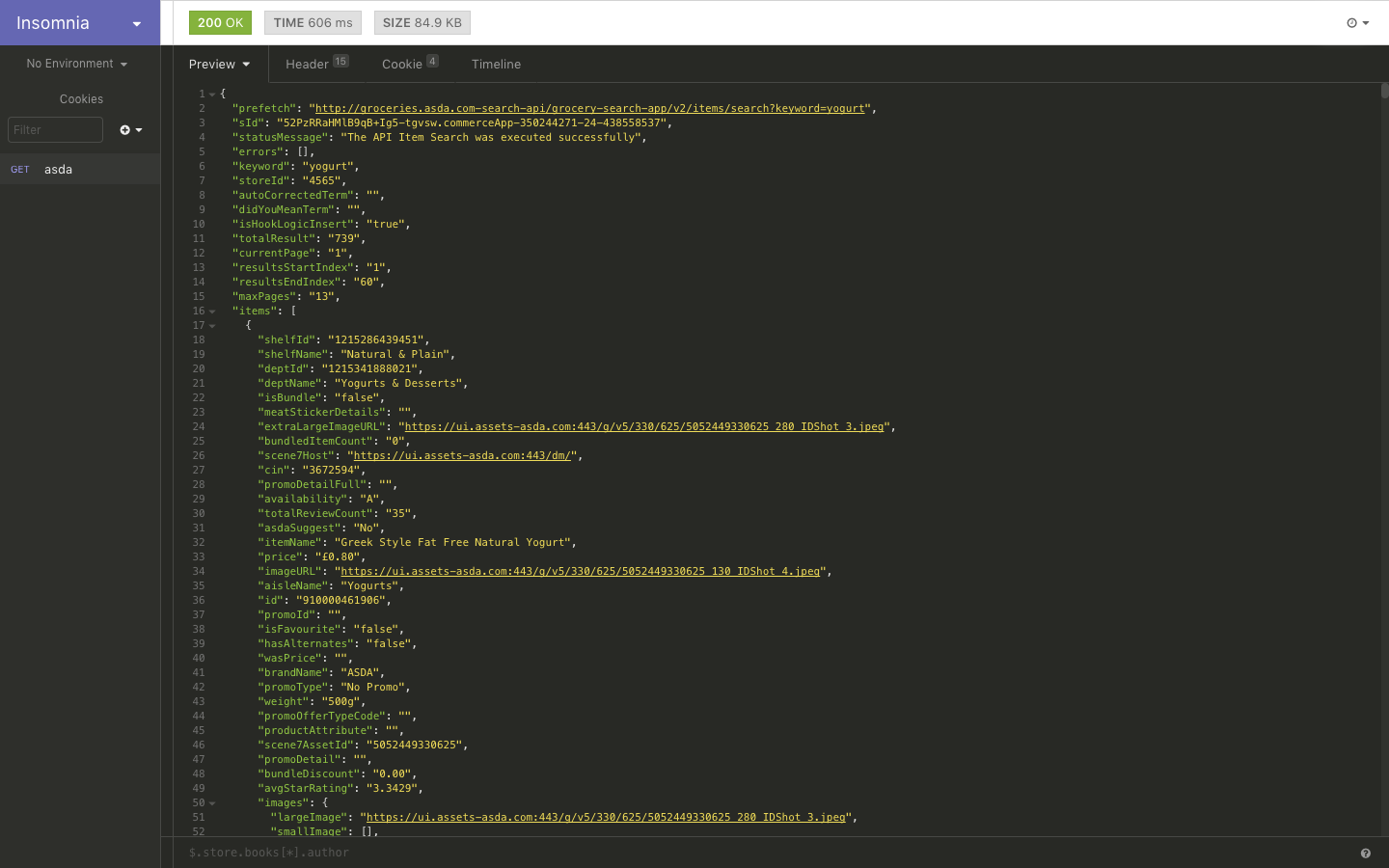 Preview of JSON response in Insomnia
Preview of JSON response in Insomnia
This example is very straight forward with no headers or security tokens required. For other cases, the REST client allows you to enter any additional response parameters that you can get from the inspect tool when gathering the request details.
Python request
We can also make the same request from python using the urllib.request library in the same way that we connect to a web page before scraping.
The JSON response can be made more readable by adding a few parameters for indenting and sorting the keys so that we can now open the file and see the response data provided to the webpage when a search is made.
# import json library
import json
# request url
urlreq = 'https://groceries.asda.com/api/items/search?keyword=yogurt'
# get response
response = urllib.request.urlopen(urlreq)
# load as json
jresponse = json.load(response)
# write to file as pretty print
with open('asdaresp.json', 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(jresponse, outfile, sort_keys=True, indent=4)
For now, we will keep all the data. My next tutorial will cover data structures and output in more detail so we can manipulate the JSON and find the relevant data.
Summary
This tutorial has outlined some of the methods we can use to scrape web pages that use javascript. These methods include:
Using a web driver to scrape content
-
Using selenium web driver to connect to a web page either with Firefox web driver, PhantomJS, headless browser
-
Use the web driver to find the elements of interest
-
Loop over the results and saving variables of interest
-
Saving data to a dataframe
-
Writing to a csv file
Make a HTTP request
-
Inspect the web page to find HTTP request details
-
Make the GET request using either a browser, REST client, python
Whilst the HTTP request method is quicker to implement in this tutorial and provides all the data we need from one request, this is not always the case. Not all websites will make their requests visible, additional security may be in place with expiring authentication tokens or the output data may require significant cleaning which would be more work than using a web driver with some javascript to enable loading all results and looping over all pages. This tutorial provides a few different alternatives you can try to make it possible to scrape javascript.
In my next tutorial we will explore data structures, manipulating data and writing to output files or databases.
This article was originally published on Medium.
Kerry Parker
Data Engineer with PhD in Physics. Interested in all things data, personal development and productivity, see more posts on Medium.

